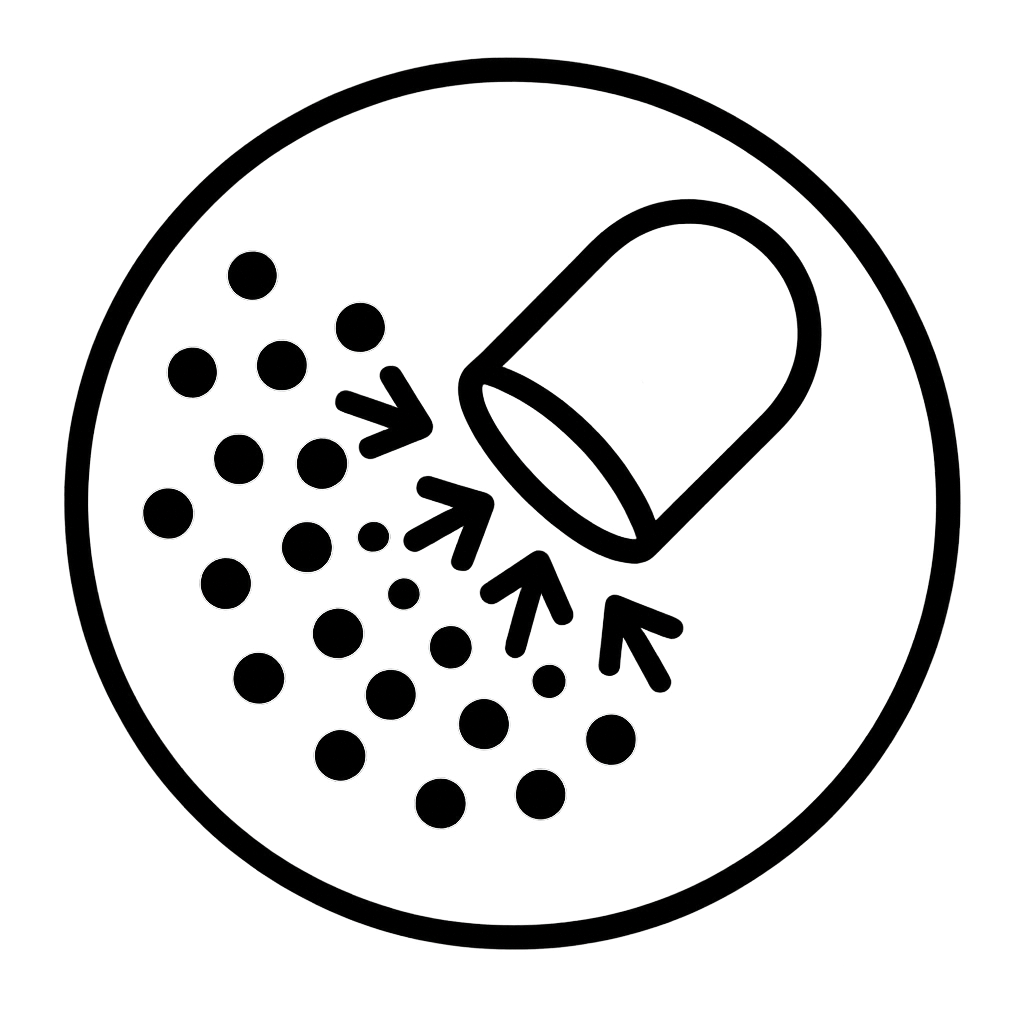
Ten research-backed strains of gut probiotic strains with 20 billion active cultures to help repopulate healthy gut bacteria to support healthy digestion, immunity, and reduced cramping/bloating while providing essential digestive enzymes that promote gut, skin, and hair health
WILD PREBIOTICS, PROBIOTICS, and DIGESTIVE ENZYMES: New from Wild Foods, this breakthrough supplement is for women and men looking to enjoy all of the benefits unique to premium strains of prebiotics, probiotics, and digestive enzymes.
IMMUNE SUPPORT & DIGESTIVE HEALTH BENEFITS: Supports healthy digestion, immunity, and reduced cramping/bloating. Provides essential digestive enzymes that promote gut, skin, and hair health.
Encourages whole body health: A healthier gut equals a healthier you. Studies show that 70% of our immune system lives in our gut, and by supporting your digestive system daily with Wild Prebiotics and Probiotics, works to keep you in tip top shape
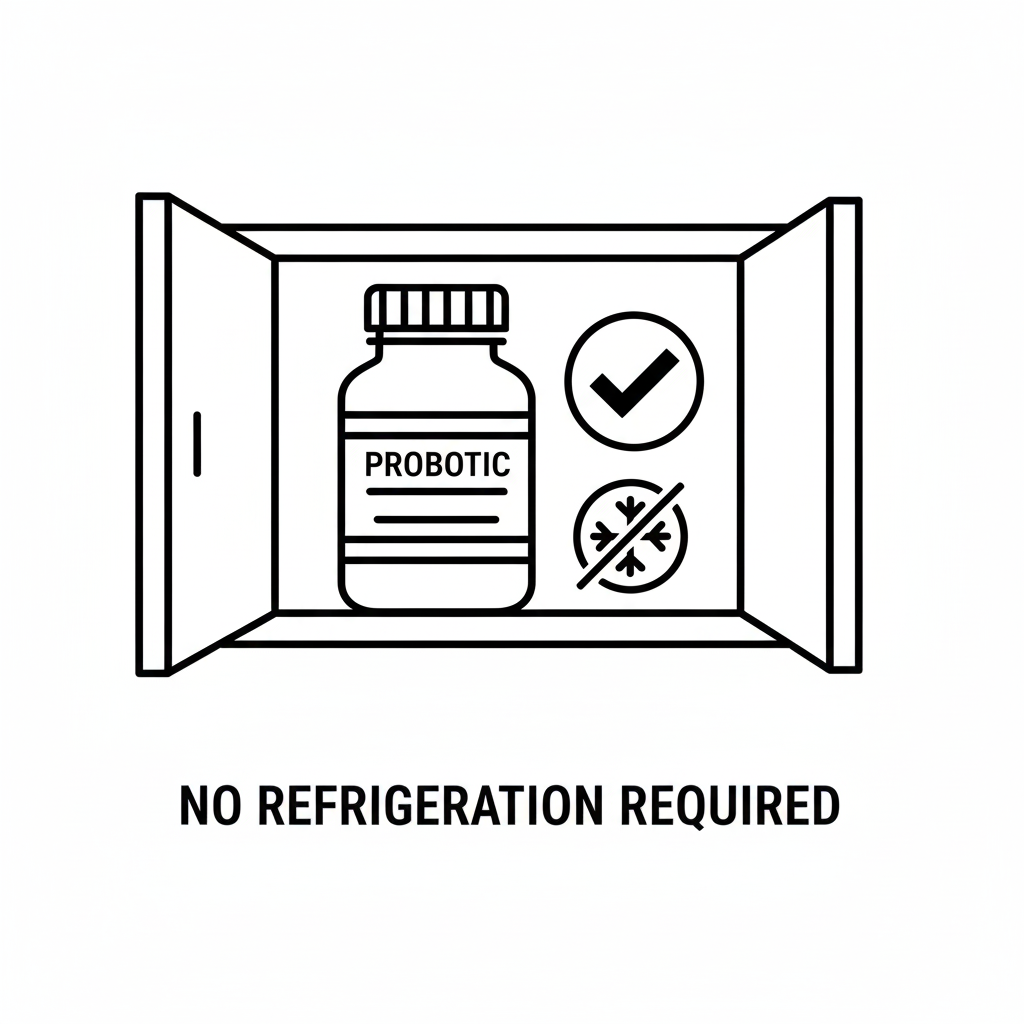
No refrigeration necessary: Freeze-dried cultures are extremely shelf-stable.
HOW TO TAKE: Take (1) one capsule daily with water.